Have you noticed some of your blog posts mysteriously slipping down Google’s rankings, even as you publish more and more high-quality content? You might be working against yourself without realizing it. If you’re uncertain about which of your pages are ranking for which keywords—and whether they might be competing—you could be suffering from something called keyword cannibalization. In this in-depth guide, you’ll learn exactly how to do a keyword cannibalization audit, why it matters for your SEO, the most effective step-by-step process, real use cases, and actionable solutions rooted in data from the industry’s top experts. Whether you’re running a blog, an ecommerce site, or an agency, this guide will help you uncover, fix, and prevent content cannibalization so every page can reach its full ranking potential.

What is Keyword Cannibalization & Why Does it Matter?
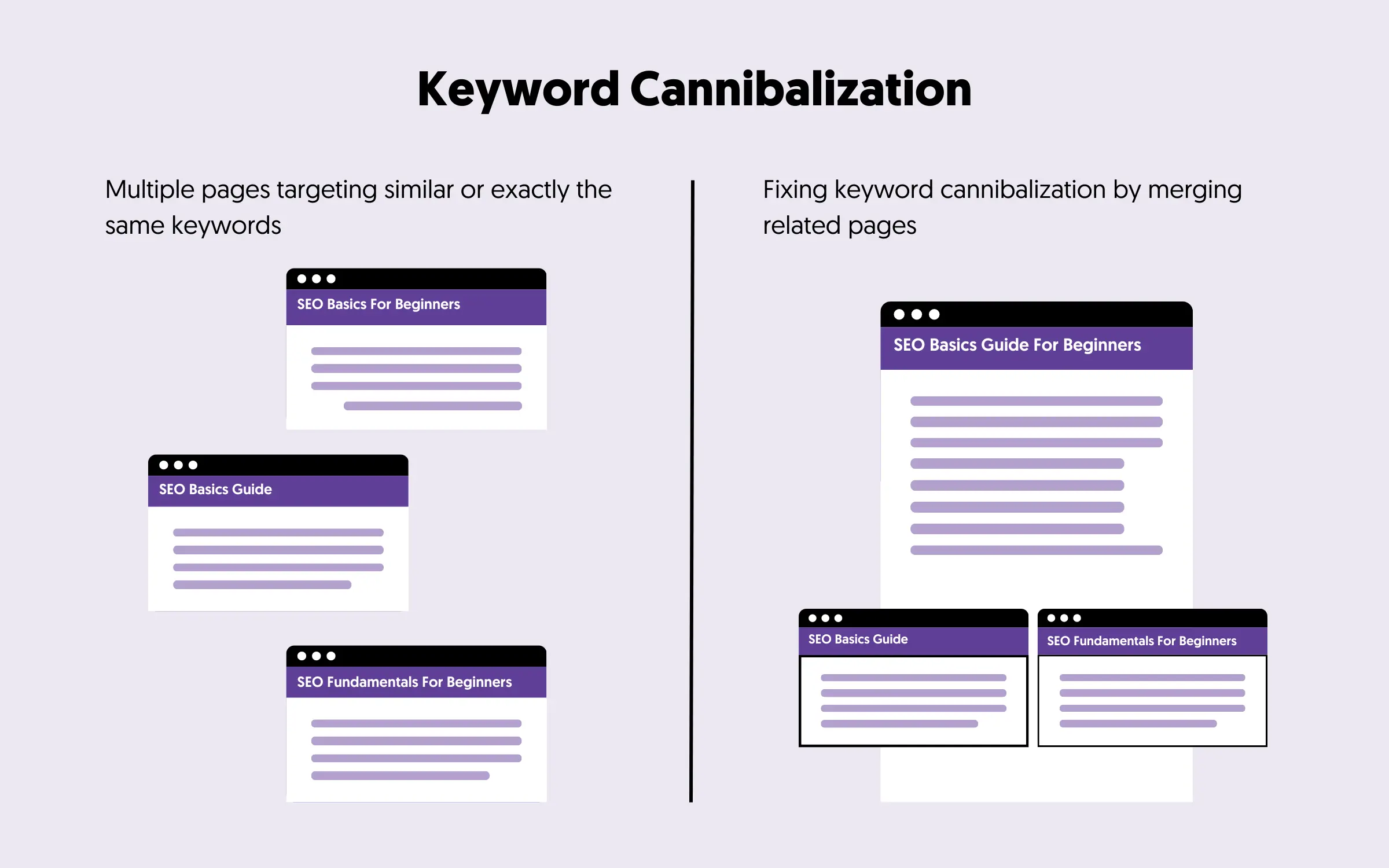
Keyword cannibalization refers to a situation where multiple pages on your site target the same or very similar keywords. Instead of strengthening your ranking, these pages end up competing with—and undermining—each other in Google’s eyes. This confusion makes it difficult for search engines to determine which page to display, which can seriously hurt your organic visibility, traffic, and conversions.
Imagine you have five blog posts, all trying to rank for “best SEO tools.” Instead of one strong page, you have five weak pages fighting each other. This dilutes authority and, often, none ranks well.
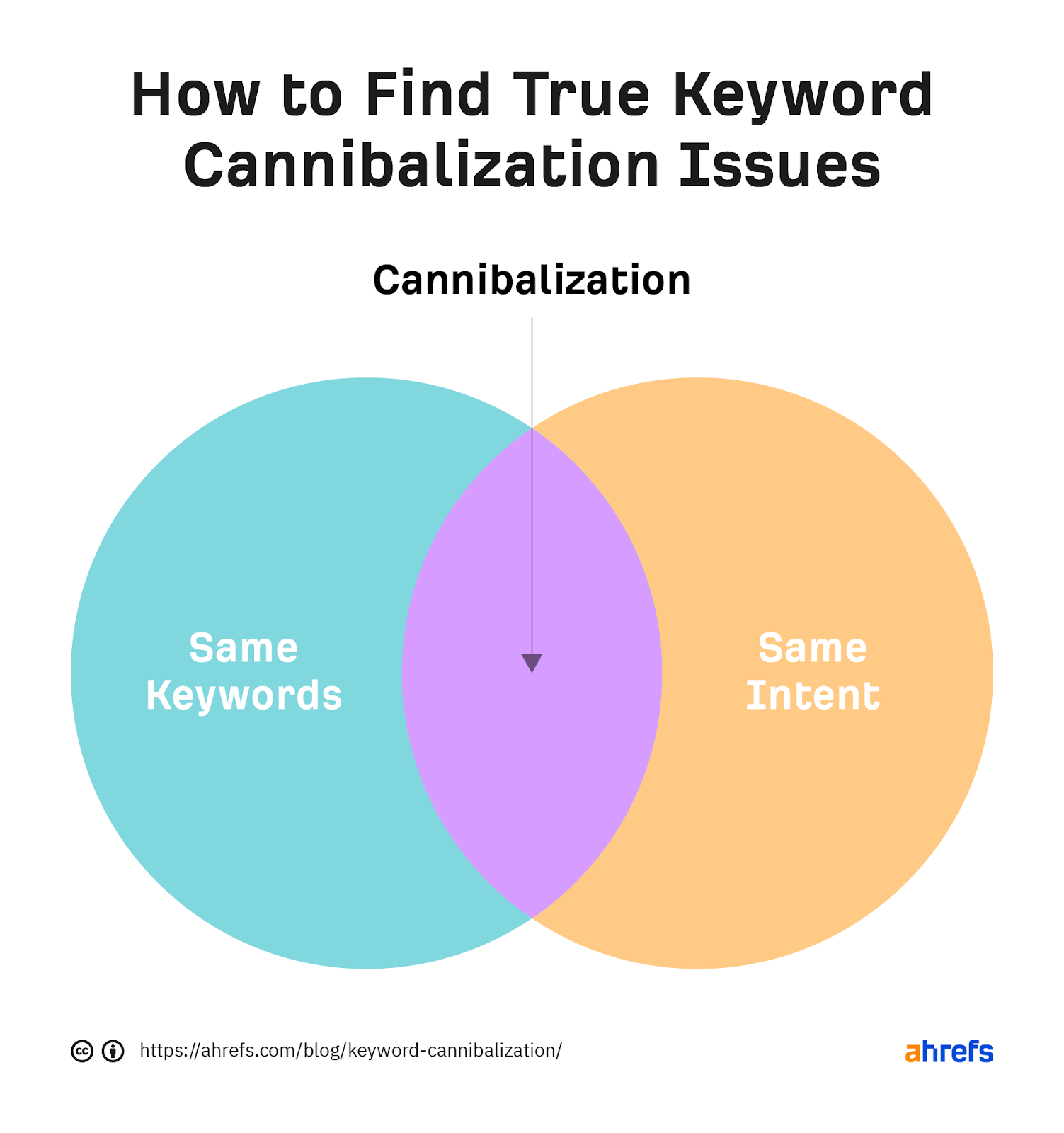
If you’ve invested time in keyword research and quality content, keyword cannibalization can quietly sabotage your SEO wins. That’s why knowing how to do a keyword cannibalization audit is so critical for every content creator, marketer, and website owner.
The Hidden Costs and Powerful Benefits of Fixing Cannibalization
Tackling keyword cannibalization provides important SEO benefits, including:
- Improved Rankings: Consolidating cannibalized pages boosts the most relevant page’s authority and ranking potential.
- Higher Organic CTR: When a single strong page ranks higher, it gets more qualified clicks.
- Better User Experience: Users find what they need more quickly, reducing confusion and bounce rates.
- Optimized Crawl Budget: Search engines index and rank your key content efficiently.
- Increased Conversions: Focusing users on authoritative pages increases lead and sales opportunities.
Ignoring cannibalization can lead to:
- Lower search rankings due to split link equity
- Fluctuating page positions in the SERPs
- Missed keyword opportunities
- Poor ROI on your content investment
- Complicated website analytics
When & Where Does Keyword Cannibalization Happen? (Use Cases & Examples)
Cannibalization can sneak into all kinds of sites—including:
- Blogs: Multiple articles cover the same topic or long-tail keyword (e.g., “SEO tips for beginners” vs. “Beginner SEO tips 2024”).
- Ecommerce Sites: Several product or category pages optimized for the same search terms (e.g. “women’s black dress” appearing on product, sub-category, and blog pages).
- Service Businesses: Landing pages for different locations or services that target the same broad keywords (e.g., “website design London” and “London web design”).

Real-world keyword cannibalization examples:
- Blogger: Writes “Best Keyword Research Tools,” “Keyword Tools for SEO,” and “Top SEO Tools”—all target the same user intent.
- Ecommerce: Multiple product variations (e.g., “red shoes,” “shoes in red,” “red running shoes”) compete as separate pages instead of being unified.
- Agency: Publishes separate service pages and blog posts, both optimized for “SEO audit,” diluting their ability to rank.
- SaaS Site: A features page, pricing page, and blog article all target “competitor analysis tool” independently, splitting their ranking power.
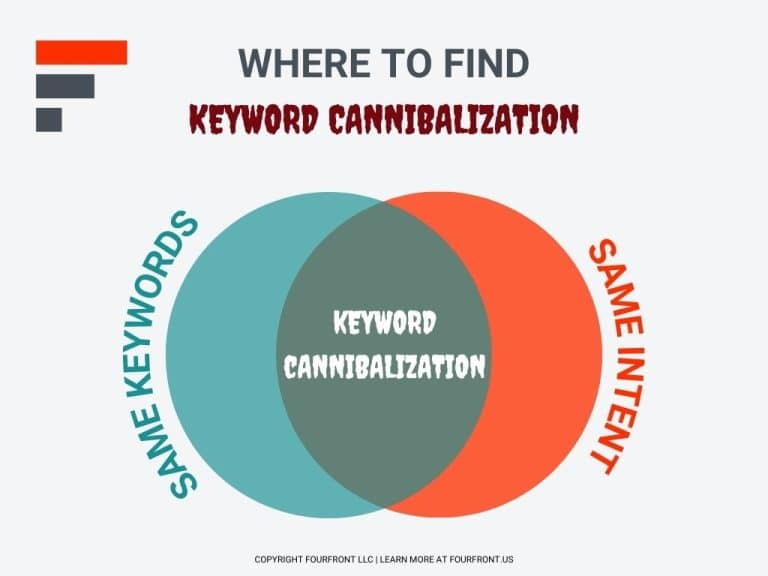
How to Do a Keyword Cannibalization Audit: Step-by-Step Process
Learning how to do a keyword cannibalization audit is a foundational SEO skill. Here’s a proven step-by-step workflow (used by expert teams at Yoast, Ahrefs, and Semrush):
Step 1: Gather Your Keyword Data
Export a list of landing pages and their primary keywords from Google Search Console, Semrush, Ahrefs, or Moz. (Google Search Console’s “Performance” report makes this easy.) List URLs and all keywords each page ranks for.
Step 2: Identify Duplicate or Overlapping Keywords
In a spreadsheet, filter to show keywords appearing in more than one URL. These are potential cannibalization cases. Use conditional formatting for visibility.
Step 3: Review Ranking Positions
Check which pages are ranking highest for each cannibalized keyword. If rankings flip-flop, or no page is high, this signals a problem.
Step 4: Analyze Content & Intent
Open competing pages side by side. Are they similar in topic, search intent, or targeting the same reader’s need? Check headings, titles, and content overlap.
Step 5: Decide on a Fix
- Merge pages: Combine competing content and 301 redirect weaker URLs.
- Noindex/Canonical: Add a canonical tag to the strongest page, or “noindex” duplicates.
- Diversify Intent: Differentiate each page by changing its keyword focus or targeting a different user intent.
- Internal Linking: Use links to point to the primary page as the authority.

Step 6: Monitor Your Results
Track keyword positions, organic traffic, and page performance. Adjust based on results—a successful fix usually shows a ranking boost in a few weeks.
Pro Tip:
Repeat this audit quarterly or after major updates to your site structure or blog content. Even great sites develop new cannibalization issues over time!

Common Challenges, Myths & Objections About Cannibalization
Addressing misconceptions is vital to auditing effectively. Let’s bust some common myths:
- Myth: “Ranking for the same keyword on two pages is always bad.”
Fact: Rarely, you can dominate SERPs with multiple results—but more often, both pages underperform. - Myth: “Keyword cannibalization only happens on big sites.”
Fact: Even small blogs and startups can face issues after 10–20 articles. - Myth: “Just change some words and it’s fixed.”
Fact: True fixes often involve merging, redirection, or intent redefinition. - Myth: “Noindexing fixes all cannibalization.”
Fact: Noindex is only helpful for out-of-date, thin, or duplicate content—sometimes merging is the best route.
Biggest challenges when auditing for cannibalization:
- Finding subtle cases where overlap is intent-based, not just word-based.
- Deciding which page to prioritize when both have decent links or traffic.
- Managing redirects and canonical tags correctly to avoid ranking losses.
- Educating content teams about intent mapping and keyword assignments.
Keyword Cannibalization Audit FAQs
1. What is a keyword cannibalization audit?
A keyword cannibalization audit is a process to detect and analyze cases where multiple pages on your website target the same keyword or user intent, causing them to compete in Google’s search results and weakening your overall SEO performance.
2. How often should I check for keyword cannibalization?
Ideally, run a keyword cannibalization audit quarterly or any time you make major content or structure updates. Rapidly growing sites may need monthly reviews.
3. Which SEO tools can find keyword cannibalization?
Leading tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, Semrush, Screaming Frog, and Moz can help identify overlapping keywords, landing pages, and ranking issues indicative of cannibalization.
4. What’s the fastest fix for cannibalization?
Combining competing content into a single, well-optimized page and redirecting weaker versions is usually the fastest, most effective fix.
5. Can blog posts and product pages cannibalize each other?
Absolutely, especially if both are optimized for similar primary keywords or answer the same search query.
6. Is using canonical tags always a good solution?
Canonical tags are helpful when content must stay live (e.g., archives), but merging and redirecting is usually better for long-term SEO authority.
7. Should I delete competing pages after merging?
You should redirect (301) those pages to the merged version to transfer authority and avoid broken links—don’t just delete.
8. How do I prevent keyword cannibalization as I publish new content?
Keep a master content map and assign primary keywords before drafting new posts, ensuring each has a unique target and intent.
9. Can a site have healthy keyword cannibalization?
In rare cases—like dominating Google with sitelinks or multiple relevant results—slight cannibalization is beneficial, but it’s the exception, not the rule.
10. Can cannibalization impact branded and non-branded keywords differently?
Yes, cannibalization usually hurts non-branded (competitive) keywords more than branded ones, but auditing both ensures best SEO results.
Conclusion: Mastering Your Keyword Cannibalization Audit
If you want to unlock your website’s full potential and climb the SERPs, knowing how to do a keyword cannibalization audit is an essential skill. From blogs and ecommerce sites to landing pages and guides, keyword overlap can erode your Google rankings and limit your growth. By systematically auditing your pages, detecting cannibalization, and applying the right fixes—merging, redirecting, canonicalizing, or refining keyword focus—you’ll build content that Google (and your audience) loves.
Ready to take your SEO to the next level? Start your content audit today, bookmark this guide, and revisit these steps often. For ongoing SEO mastery, check out resources from Yoast’s Keyword Cannibalization Guide, Ahrefs, and Victorious SEO. Let no keyword (or ranking!) go to waste on your site.
Start your audit now—your higher rankings are waiting!
